Cable To Connect Graphics Card To Motherboard
When it comes to harnessing the power of a graphics card, the cable that connects it to the motherboard plays a vital role. The right cable can ensure a seamless connection and maximum performance, while the wrong one can result in compatibility issues and diminished visual output.
A well-designed cable to connect a graphics card to the motherboard combines reliability and high-speed data transfer, allowing for smooth gameplay, efficient video editing, and crisp visuals. With advancements in technology, these cables have evolved to support higher resolutions, multiple displays, and fast refresh rates. They have become an integral component of any gaming or multimedia setup, enabling users to unlock the full potential of their graphics cards.
When connecting a graphics card to a motherboard, you will need a compatible cable to ensure a proper connection. The most common cable used for this is the PCIe (PCI Express) cable. This cable provides a high-speed link between the graphics card and the motherboard, allowing for fast data transfer and optimal performance. Ensure that the cable is securely connected to both the graphics card and the PCIe slot on the motherboard for a reliable connection. This cable is essential for gamers and professionals who rely on a high-performance graphics card.

Exploring Different Cable Options to Connect Graphics Card to Motherboard
When it comes to setting up a powerful and efficient gaming or video editing rig, one component that plays a crucial role is the graphics card. The graphics card, also known as the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), handles the rendering of images, videos, and animations on your computer. To connect the graphics card to the motherboard, you need the right cables. In this article, we will explore the different cable options available to connect your graphics card to the motherboard, their functionalities, and how to choose the right one for your system.
1. PCIe Power Connectors
In most cases, graphics cards require additional power to function properly. To provide power to the graphics card, PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) power connectors are used. These connectors come in two forms: 6-pin and 8-pin. They deliver power directly from the power supply unit (PSU) to the graphics card.
The 6-pin PCIe power connector provides up to 75 watts of power, while the 8-pin PCIe power connector can deliver up to 150 watts of power. Some high-end graphics cards may require dual 8-pin power connectors for optimal performance. It is essential to check the power requirements of your graphics card and ensure that your power supply unit has the necessary PCIe power connectors.
To connect the power connectors to the graphics card, locate the appropriate connectors on the graphics card and connect the corresponding cables from the PSU. Make sure to align the notches on the connectors to ensure a secure and proper connection. Once connected, you can power on your system, and the graphics card should receive the necessary power to function.
1.1 GPU Power Cables and Adapters
GPUs often come with their power cables included in the package. These cables are specifically designed to work with the graphics card and are compatible with the appropriate PCIe power connectors. However, in some cases, you may need to use adapters or purchase additional power cables separately.
When using adapters or additional power cables, it is crucial to ensure their compatibility with your graphics card and power supply unit. Using incompatible cables or adapters may lead to inadequate power delivery or other issues that can affect the performance and stability of your graphics card.
It is recommended to use the cables and adapters provided by the graphics card manufacturer or trusted third-party brands that specialize in PC components. These cables and adapters undergo rigorous testing to ensure compatibility and safety.
2. DisplayPort and HDMI Cables
Once the graphics card is properly powered, the next step is to connect it to your display device, such as a monitor or a TV. The most common cables used for this purpose are DisplayPort and HDMI cables. Both cables transmit audio and video signals, allowing you to enjoy high-quality visuals and audio.
DisplayPort and HDMI cables support different maximum resolutions and refresh rates. DisplayPort cables generally offer higher bandwidth and are suitable for gaming and video editing purposes. They support higher resolutions (up to 8K) and refresh rates (up to 240Hz), making them ideal for gamers and professionals who require smooth and responsive visuals.
HDMI cables, on the other hand, are widely used for basic computing and multimedia applications. HDMI cables can support resolutions up to 4K and refresh rates up to 60Hz. They are commonly found on TVs, monitors, and other consumer electronic devices.
When selecting the appropriate cable, consider the specifications of your graphics card and display device. Check the available ports on both the graphics card and the display device, and ensure compatibility with the cable type. Additionally, if you require specific features such as HDR (High Dynamic Range) or FreeSync/G-Sync support, make sure the cable you choose can accommodate these features.
2.1 Choosing the Right Cable Length
When it comes to cable length, it is essential to choose the appropriate length to avoid unnecessary clutter and signal degradation. If the distance between your graphics card and the display device is short, a standard length cable should suffice. However, if you need to cover longer distances, you may need to invest in longer cables or consider using signal repeaters or extenders.
Excessively long cables can result in signal degradation, causing visual artifacts and decreased image quality. It is recommended to use cables that are within the recommended length specified by the cable manufacturer or seek professional advice if you are unsure about the optimal cable length for your setup.
3. DVI and VGA Cables
While DisplayPort and HDMI cables have largely replaced older cable options, such as DVI (Digital Visual Interface) and VGA (Video Graphics Array) cables, there are still scenarios where these older cables may be necessary. Some older displays or projectors may only have DVI or VGA ports, requiring the use of compatible cables.
DVI cables support both digital and analog signals and are capable of transmitting high-resolution video. They come in different variants, including DVI-D (digital only), DVI-A (analog only), and DVI-I (integrated digital and analog). VGA cables, on the other hand, transmit analog signals and are commonly found on older display devices.
If you need to connect your graphics card to a device that only supports DVI or VGA, you can use a DVI-to-DVI or VGA-to-VGA cable. Alternatively, there are also DVI-to-HDMI and VGA-to-HDMI adapters available, allowing you to connect your graphics card to an HDMI port using the appropriate cable or adapter.
3.1 Quality and Signal Compatibility
When using DVI or VGA cables, it is crucial to ensure the quality of the cables and their compatibility with your graphics card and display device. Poor-quality cables may result in signal degradation, leading to visual artifacts or no display at all. Additionally, not all graphics cards support analog signals, so make sure to check the specifications of your graphics card before using VGA cables.
If possible, it is recommended to use digital connections, such as DisplayPort or HDMI, for superior image quality and compatibility. However, if you must use DVI or VGA cables, opt for high-quality cables from reputable manufacturers to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Understanding the Importance of Proper Cable Connections
Proper cable connections between the graphics card and the motherboard are essential for ensuring optimal performance and stability. Incorrect or loose cable connections can lead to issues such as artifacts, flickering, or even system crashes. Here are some key reasons why proper cable connections are crucial:
- Power Delivery: The PCIe power connectors provide the necessary power for the graphics card to function properly. Without a secure and proper connection, the graphics card may not receive adequate power, leading to performance issues or system instability.
- Data Transfer: Display cables like DisplayPort or HDMI transmit both audio and video signals between the graphics card and the display device. Loose or faulty connections can result in signal loss, visual artifacts, or no display at all.
- Compatibility: Using the appropriate cables ensures compatibility between the graphics card, motherboard, and display device. Different graphics cards and monitors may have different port types, and using incorrect cables can result in non-functional connections.
- Signal Quality: Poor-quality cables or excessive cable lengths can degrade the signal quality, resulting in decreased image quality or unstable refresh rates. It is important to use high-quality cables of the appropriate length to maintain optimal signal integrity.
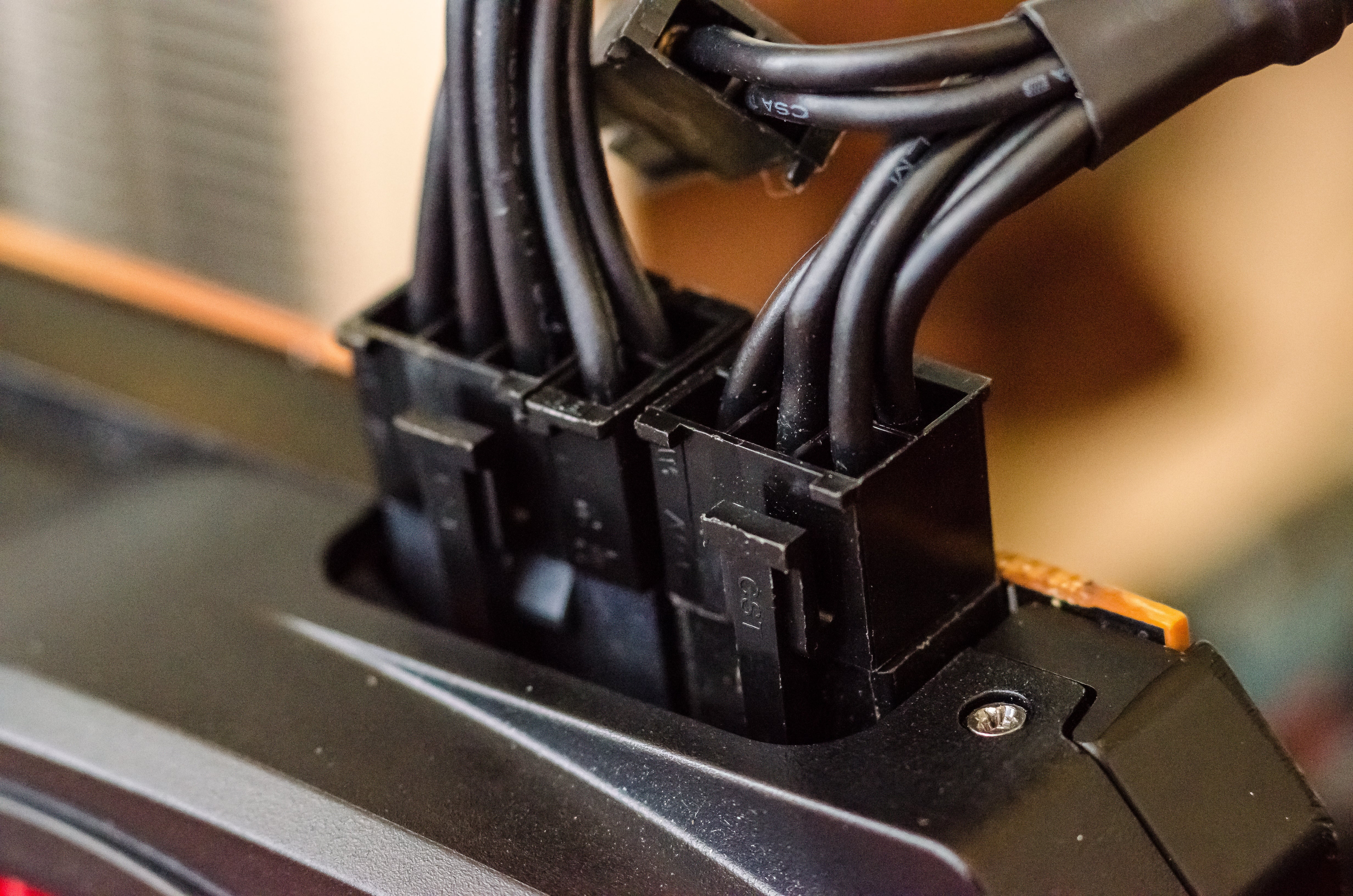
Cable to Connect Graphics Card to Motherboard
When it comes to connecting a graphics card to a motherboard, there are different types of cables that can be used. The specific cable needed depends on the graphics card and motherboard connectors.
The most common cable for connecting a graphics card to a motherboard is the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) cable. This cable is used to provide a high-speed connection between the graphics card and motherboard. It comes in different versions, such as PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 4.0, with varying speeds and bandwidth.
When connecting a graphics card to a motherboard, it is important to ensure that the cable is properly inserted into the corresponding slots on both the graphics card and motherboard. Improper connection or loose cables can result in poor performance or no display at all.
Additionally, some graphics cards and motherboards may require additional power cables for proper operation. These power cables are typically included with the graphics card and need to be connected to the power supply unit (PSU) to provide sufficient power to the graphics card.
In summary, the PCIe cable is the most common cable used to connect a graphics card to a motherboard. It is important to ensure proper insertion and connections to avoid any issues or performance issues.
Cable to Connect Graphics Card to Motherboard
- The primary cable used to connect a graphics card to a motherboard is the PCIe connector.
- The PCIe connector provides a high-speed data transfer between the graphics card and motherboard.
- The cable connects to the PCIe slot on the graphics card and the PCIe slot on the motherboard.
- It is essential to choose a cable that matches the version of PCIe supported by the graphics card and motherboard.
- Proper installation of the cable ensures a stable connection and optimal performance of the graphics card.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about the cable used to connect a graphics card to a motherboard:
1. What type of cable is required to connect a graphics card to a motherboard?
To connect a graphics card to a motherboard, you will need a PCI Express (PCIe) cable. This cable is specifically designed to provide high-speed communication between the graphics card and the motherboard. PCIe cables come in various lengths, so ensure you choose the appropriate length for your setup.
It's important to note that the graphics card and motherboard must have compatible PCIe slots for the cable to be properly connected.
2. Are there different types of PCIe cables?
Yes, there are different versions of PCIe cables, including PCIe 1.0, PCIe 2.0, PCIe 3.0, and PCIe 4.0. The version you need will depend on the compatibility of your graphics card and motherboard. It's essential to ensure that both the graphics card and motherboard support the same PCIe version to establish a stable connection.
It's worth noting that the newer versions of PCIe offer faster communication speeds and improved performance compared to the older versions.
3. How do you connect the PCIe cable to the graphics card and motherboard?
Connecting the PCIe cable to the graphics card and motherboard is a simple process. First, identify the PCIe slot on the motherboard and the corresponding slot on the graphics card. Align the notches on the cable connector with the slot on the graphics card and gently press it in until it locks in place.
Repeat the same process for the PCIe slot on the motherboard. Make sure the cable is securely connected on both ends to ensure stable communication between the graphics card and the motherboard.
4. Is it possible to use an adapter to connect a different cable to the graphics card and motherboard?
Yes, it is possible to use an adapter, but it is recommended to use the appropriate PCIe cable for the best performance and compatibility. Using adapters may introduce compatibility issues or degrade the performance of the graphics card.
If you have a specific requirement to use an adapter, make sure to choose a high-quality adapter that supports the desired cable types and maintains the necessary bandwidth for optimal performance.
5. Can I daisy-chain multiple graphics cards using a single cable?
No, it is not recommended to daisy-chain multiple graphics cards using a single cable. Each graphics card should have its own dedicated PCIe cable connected directly to the motherboard to ensure sufficient power and data bandwidth.
Daisy-chaining multiple graphics cards with a single cable can lead to insufficient power supply, data transmission issues, and instability in the system.
In conclusion, the cable needed to connect a graphics card to a motherboard is known as a PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) cable. This cable is essential for establishing a connection between the graphics card and the motherboard, allowing the graphics card to send and receive data effectively.
The PCIe cable comes in various versions, such as PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 4.0, with each version offering different speeds and bandwidths. It is important to ensure that the graphics card and motherboard are compatible with the same PCIe version to ensure optimal performance.































